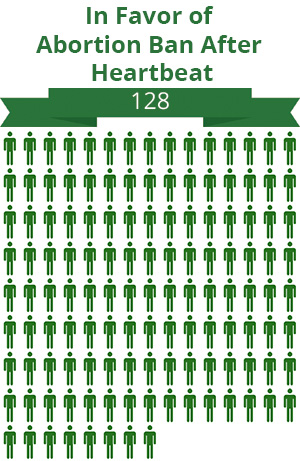
Abortion ban after fetal heartbeat detected?
Earlier this month, Ohio passed a bill banning abortion after a fetal heartbeat has been detected. Mississippi recently passed a similar bill. Both laws go into effect July 1, 2019. Courts have blocked similar laws in Kentucky and North Dakota.
When does a fetal heartbeat begin?
A fetal heartbeat can begin as early as six weeks into pregnancy, which means these are among the strictest abortion regulations in the United States.
By comparison, New Hampshire does not impose any restrictions on abortion based on a woman’s stage of pregnancy. The U.S. Supreme Court ruling Roe v. Wade allows states to regulate abortions after a fetus is able to survive outside the womb, but generally not earlier.
Pros and Cons
Proponents of banning abortion once a fetal heartbeat has been detected argue that a beating heart is synonymous with human life and personhood. Despite the fact that the fetus has not yet fully formed at that stage, a heartbeat indicates that it is a distinct life from its mother and therefore deserves to be protected.
Opponents argue that, because a fetus with a newly-detected heartbeat hasn’t yet formed other vital organs like lungs, there is no chance of it being able to live outside of its mother. Therefore, the woman should still have a right to choose. Others argue that such a law would open New Hampshire up to lawsuits on constitutional grounds, since Roe v. Wade requires abortions to be legal before a fetus can survive outside the womb.
Should New Hampshire ban abortion after a heartbeat has been detected?
Discussion held on Citizens Count website and Facebook page April 18, 2019